![]()
1. Select all the trees in the database.
2. Build a buffer zone of four metres around each tree.
3. Retrieve the utility poles within this buffer zone. They are the poles too close to the trees.
This analysis is different from the previous one is that no user-defined attributes will be used. That is to say, all the analysis will be performed using only system-defined attributes. We could have created databases for the trees and utility poles as well.
![]() Disconnect
from the DB Manager.
Disconnect
from the DB Manager.
In this exercise, we will be working with tree features without any user-defined attributes. To prevent the GIS from searching the user-defined database, the DB Manager will be disconnected from the Information Manager.
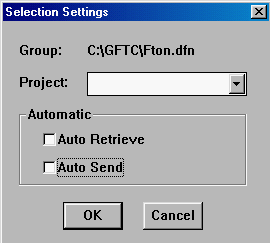
1. Select the Options > Display > Projects ... menu item.
2. A Selection Settings panel will appear showing that the Information Manager is currently connected to the Info_Manager database tables.
Use the cursor to select "Info_Manager" in the Project field and press the Delete key on the keyboard to delete it. Also turn off Auto Retrieve and Auto Send to disconnect the two databases.
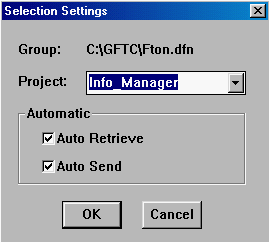
2. Click on the OK button
.
NOTE : To connect with the Info_Manager database again, simply return the Selection Settings panel to its previous state.
![]() Generate
buffer zones around all trees.
Generate
buffer zones around all trees.
1. Make sure that the DB Manager has been disconnected.
2. Use the Visibility Parameter Buttonor the Options > Display > Visibility Parameters ... menu item to show trees (feature code is TREE).
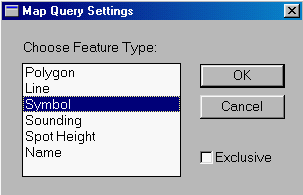
3. Select the MapQuery > By User Defined Area ... menu item.
4. A Map Query Settings panel appears. Select Symbol to indicate that you will be selecting symbol features within the area.
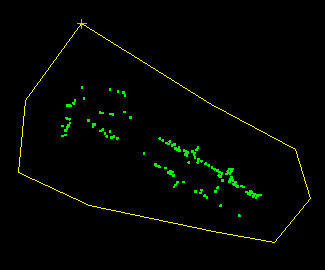
5. Draw a polygon around the trees to select all of them.
6. You might want to highlight the selection to make sure that all trees have been selected.
7. Generate a four-metre buffer zone around the current selection. Call the zone TREES. Use a resolution of one metre.
![]() Retrieve
utility poles within the zone.
Retrieve
utility poles within the zone.
1. Display only utility poles (feature code is UTILITY_POLE).
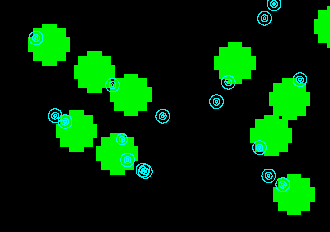
2. Select the MapQuery > By Zone ...menu item to overlay the zone TREES over the utility poles, which are point symbols.
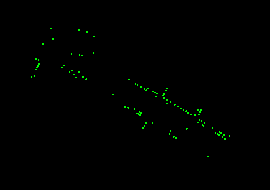
3. A message at the bottom of the window indicates that there are 30 utility poles within four metres of any tree.
4. This is a display of some of the utility poles that are too close to trees.
(288824, 740226), 1:300
![]() How many trees are too close to the
utility poles ?
How many trees are too close to the
utility poles ?
We have found out that there are 30 utility poles too close to the trees.
How many trees are too close to the poles ? Will there be 30 of them as
well ?
![]() Overlay of
zone over points.
Overlay of
zone over points.
Out of overlays of zone over zone, over line, and over point, overlay of zone over point is the simplest. The zone is stored in raster format, and the pixels belonging to the zone are known. To find out if a point feature is overlapping a zone, we need only to check if a pixel in the zone already exists at that location. If the zone is a vector polygon, many more computations would have to be performed to determine whether a point is inside it or not. For an explanation, please consult the technical note in the chapter on Use Topology to Identify Polygons by Pointing.
![]()