![]()
The vector representation is good for line maps where features are represented by points or lines. Images such as aerial photographs do not use lines. Traditional cartographic techniques break down a continuous tone image into dots of various sizes to show different intensities. A similar technique in a GIS is used for digital images, resulting in a raster representation.
A raster representation is based on a regular grid, very much like the resolution grid we have described, superimposed upon the image. Each cell of the grid, called a pixel for picture element, would be assigned a colour or a gray scale. The following shows a simple black and white image of two buildings in raster format. The grid is not visible on a raster image but is shown here to illustrate the pixel size used. As in the case of the resolution grid for vector representation, the pixel size in a raster representation determines the resolution and hence the quality of the image.
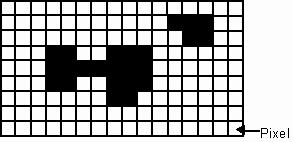
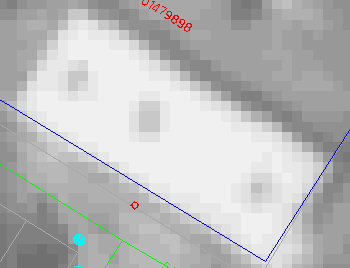
On a photographic image, a gray scale will be assigned to each pixel to
represent the intensity at that spot. The following is a much enlarged
portion of an aerial photograph. At this magnification, you will see the
staircase effect due to resolution.
![]() Display
the raster image of an aerial photograph.
Display
the raster image of an aerial photograph.
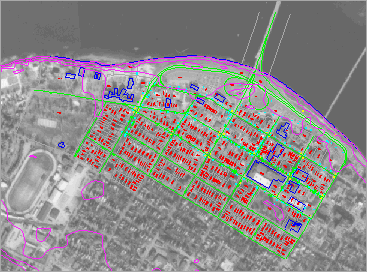
An aerial photograph can be drawn over the vector map we have been using
so far. The combined effect would be the line map superimposed over an
aerial photograph as a backdrop. This produces something like a
conventional orthophoto map, which provides both map and image information
for the same area.
1. Select the Draw > Raster Image Backdrop > Caris image <I PV> settings .. menu item.
2. The Raster Backdrop Settings panel appears.
Turn on the Single Layer switch, click on the highlighted layer (in the Layers Available area) so that number 1 appears on the list of Layers Selected, and turn on the Enable Backdrop During Vector Draw switch. Turning on the last switch allows you to draw the aerial photograph and the line map at the same time.
NOTE : Although layer 1 has already been highlighted in the list of layers available, you must still click on it to select it.
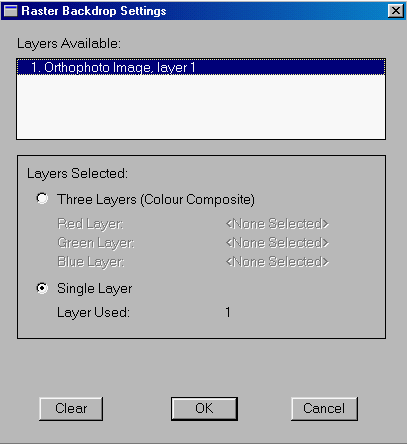
3. Click on the OK button
.
4. Select the Draw > Overview menu item or the Overview iconon the CARIS Panel to draw the entire database.
5. Zoom into an area of the image, and you will start to see the effect of resolution on raster images.
(288875,740095), 1: 400
![]()